System designers have long given hydraulic cylinder-based motion control systems first consideration in applications requiring handling of loads upwards of 1.360 kg, mostly because of the high power density of the cylinders themselves. But when the designer factors in the large space required for the intricate infrastructure needed to achieve that power, that power density becomes much less attractive.
Now, however, thanks to technology that builds hydraulic motion control into an envelope smaller than a conventional electromechanical unit, designers and end-users can enjoy the power conversion advantages of hydraulic fluids without the expense, complexity, and need to clean up after conventional hydraulic cylinder-based systems.
Electro-hydraulic linear actuators are fast becoming the motion designer’s choice over hydraulic cylinders for a wide range of heavy load handling in outdoor equipment, marine, military, aerospace and many other applications.
Structural differences
A hydraulic cylinder-based motion control system converts electrical energy into motion using an assembly involving oil reservoirs, electric motors, pumps, oil filters, relief valves, and directional valves. The speed desired and the size of the cylinder dictate the size of the pump needed, which then determines the size of all other components. The higher the required speed, the higher the cost of the system and the greater the operating space needed.
An electro-hydraulic system, in contrast, embeds the equivalent of that infrastructure into an envelope that is about the same size as a conventional electromechanical actuator. (Figure 1) An electric motor rotating clockwise turns a pump that pressurize the hydraulic fluid. Valves open to draw fluid from both the reservoir and head side, and control delivery to extend the rod. On retraction, the motor runs counterclockwise, reversing the operation, and returning the fluid to the reservoir and the opposite side of the piston. For loads of up to 2.180 kg, miniaturising that infrastructure has significant advantages over hydraulic cylinders in power density, maintenance requirements, location versatility, cleanliness and cost, while handling comparable shock loading. (Figure 2)
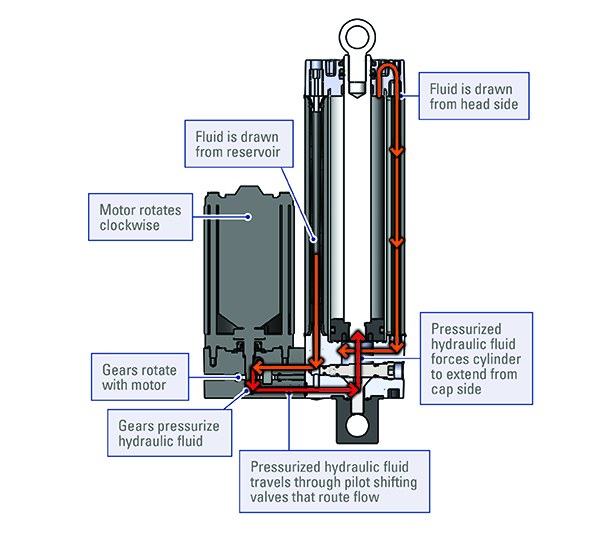
Figure 1: Extension cycle Thomson Warner Linear H-Track electro-hydraulic actuator.
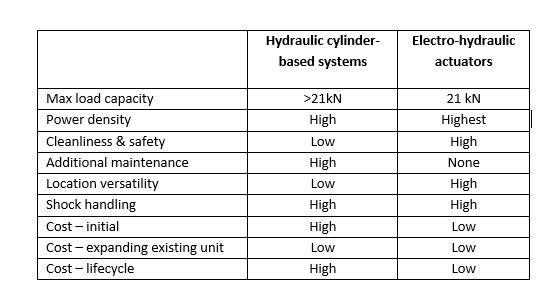
Figure 2: Comparison of hydraulic cylinder-based systems and electro-hydraulic actuators.
Load capacity
By replacing the gear and lead screw assemblies of conventional electromechanical actuators with a compact hydraulic system, electro-hydraulic actuators can move up 2.180 kg. Loads of this size have typically been relegated to hydraulic cylinder-based systems. This load range is more than 500 kg greater than the capacity of a conventional electromechanical actuator.
Power density
For raw power density, electro-hydraulic designs have a distinct advantage. While the electro-hydraulic actuator and hydraulic cylinder may not be too much different in size, the support infrastructure needed to operate the hydraulic option consumes significant space.
Cleanliness and safety
Electro-hydraulic actuators also have an advantage in cleanliness and safety. External leaks at pipe and hose fittings of hydraulic cylinder systems occur over time due to vibration and other factors. When these leaks happen, the cylinder leaks a film of oil into the plant environment with every stroke.
Internal leaks present an even greater maintenance challenge. Leaks inside the pump, pressure controls, directional valves and cylinder convert pressure and flow to heat or wasted energy, which will reduce actuator speed. In industrial settings, leaks also cause odor and present slipping hazards.
Maintenance requirements
In addition to maintenance issues related to the hydraulic fluid itself, hydraulic cylinder systems have additional maintenance demands, which increase as the cylinders begin to wear and leak around the piston. Pumps are also affected by wear, internal leaks and pressure losses of each component, including the conductors, hose and pipes. Electro-hydraulic actuators are self-contained units which require no maintenance.
Location versatility
Because they don’t need an elaborate support infrastructure, electro-hydraulic actuators make it more effective to move control closer to the point of application. Hydraulic cylinders are far less than ideal for any application that is hard to access. If a cherry picker vehicle designer wants motion control to tilt the bucket, for example, it would be far easier to run electrical wire to up the boom than hydraulic fluid transport tubing. This solution also removes potential concerns about fluid dripping into the environment.
A designer of a tractor-hauled seeding unit might output hydraulic lines to the rear of the tractor to control the depth into which the planter cuts to deposit the seed. Replacing that fluid hose with an electric cable has many advantages, such as avoiding costly infrastructure and fluid leakage into a food crop.
Shock loading
Historically, hydraulic technology has been better able to handle sudden shocks, such as the impact of a snow-covered concrete barrier on an cylinder-guided plow blade. However, embedding this technology into electro-hydraulic actuators gives them shock-loading benefits on par with hydraulic cylinders, countering any advantage they might have previously had in this area. Another example of shock handling would be a mower deck running into a large rock. As with the snowplow example, the electro-hydraulic actuator would absorb the sudden energy spike instantly by redistributing the fluids throughout the internal valves and pump housing.
Cost effectiveness
Conventional hydraulic systems are most cost effective when they are already specified into a design already containing hydraulic elements, and it is just a matter of adding cylinders to the initial design. Otherwise, there is a cost in designing the support infrastructure and incorporating that into the overall system design.
Eliminating fluid handling and storage, leak and spill management, and additional maintenance costs of identifying and repairing leaks can also reduce lifecycle costs for end-users. These benefits are marketable for OEMs and can easily be communicated as advantages to their customers.
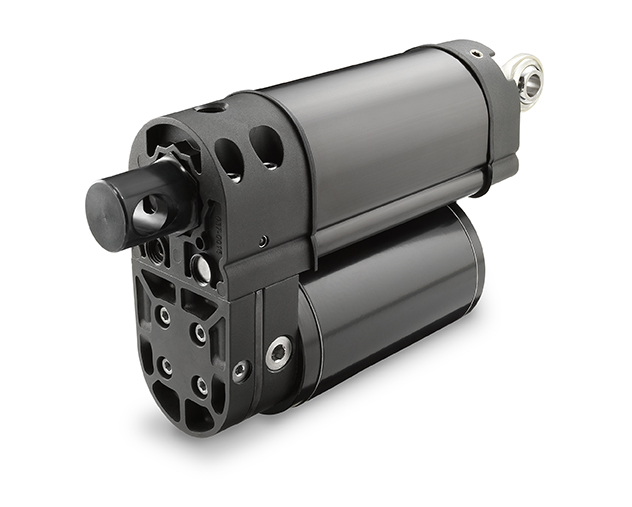

The Thomson Warner Linear H-Track electro-hydraulic linear actuator provides the performance of hydraulics without the expansive space requirements nor the prohibitive cost of full-sized hydraulic systems. It handles force up to 21.350 N and features the smallest mounting envelope in its class.
Conclusion
For new application designs requiring handling of loads up to 2.180 kg and speeds up to 100 mm (4 inches) per second, electro-hydraulic actuators have significant advantages over hydraulic cylinder-based systems in power density, cleanliness of operation, versatility and lifecycle costs. They also match hydraulic systems in load and shock handling performance.